Field Guide to Continuous Probability Distributions

Field Guide to Continuous Probability Distributions Gavin E. Crooks
v1.0.0 (2019)
[ PDF | Amazon | Preface | Index | Source code]
Over 170 continuous univariate probability distributions (and at least as many synonyms) organized into 20 families.
Preface: The search for GUD
A common problem is that of describing the probability distribution of a single, continuous variable. A few distributions, such as the normal and exponential, were discovered in the 1800’s or earlier. But about a century ago the great statistician, Karl Pearson, realized that the known probability distributions were not sufficient to handle all of the phenomena then under investigation, and set out to create new distributions with useful properties.
During the 20th century this process continued with abandon and a vast menagerie of distinct mathematical forms were discovered and invented, investigated, analyzed, rediscovered and renamed, all for the purpose of describing the probability of some interesting variable. There are hundreds of named distributions and synonyms in current usage. The apparent diversity is unending and disorienting.
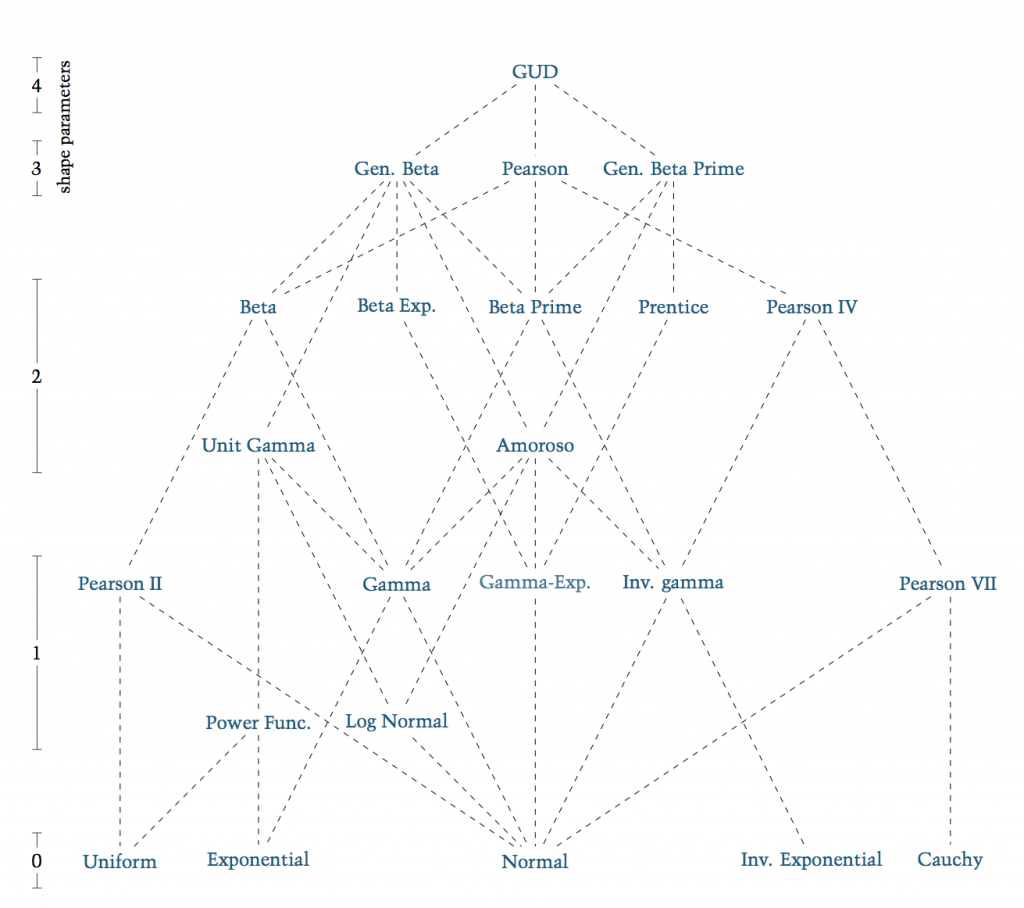
Fortunately, the situation is less confused than it might at first appear. Most common, continuous, univariate, unimodal distributions can be organized into a small number of distinct families, which are all special cases of a single Grand Unified Distribution. This compendium details these hundred or so simple distributions, their properties and their interrelations.
Hierarchy of Principle distributions
Index of Distributions
β
β′
χ
χ2
Γ
Λ
Φ
Amaroso (11.1)
anchored Amaroso
anchored exponential
anchored log-normal
anti-log-normal
arcsine (12.6)
Appell Beta (20.17)
ascending wedge
ballasted Pareto
Bates (21.1)
bell curve
beta (12.1)
beta, J shaped
beta, U shaped
beta-exponential (14.1)
beta-Fisher-Tippett (21.2)
beta-k
beta-kappa
beta-logistic (15.1)
beta-log-logistic
beta type I
beta type II
beta-P
beta-pert
beta-power
beta-prime (13.1)
beta-prime exponential
biexponential
bilateral exponential
Birnbaum-Saunders (21.3)
biweight (12.10)
BHP (8.7)
Box-Tiao
Bramwell-Holdsworth-Pinton
Breit-Wigner
Brody
Burr (18.3)
Burr type I
Burr type II (15.2)
Burr type III
Burr type XII
Cauchy(9.6)
Cauchy-LorentzCauchy
centered arcsine(12.7)
central-beta(12.5)
central-logistic(15.4)
Champernowne
chi(11.8)
chi-square(7.3)
chi-square-exponential (8.3)
circular normal
Coale-McNeil
Cobb-Douglas
compound gamma
confluent hypergeometric (20.12)
Dagum(18.4)
Dagum type I
de Moivre
degenerate
delta
descending wedgeSee wedge (5.4)
Diracde
double exponential
doubly exponential
doubly non-central F
Epanechnikov (12.9)
Erlang
error
error function
exponential(2.1)
exponential Burr
exponential gamma
exponential generalized beta type I
exponential generalized beta type II
exponential generalized beta prime
exponential power (21.4)
exponential ratio (5.7)
exponentiated exponential (14.2)
exponentiated Weibull
extended Pearson (20.2)
extreme valueGumbel
extreme value type N
F (13.3)
F-ratio
fatigue life distribution
Feller-Pareto
Fisher-F
Fisher-Snedecor
Fisher-Tippett (11.25)
Fisher-Tippett type I
Fisher-Tippett type II
Fisher-Tippett type III
Fisher-Tippett-Gumbel
Fisher-z
Fisk
flat
folded normal
Fréchet (11.29)
FTG
Galton
Galton-McAlister
gamma (7.1)
gamma-exponential (8.1)
gamma ratio
Gaussian
Gauss
Gauss hypergeometric (20.11)
generalized arcsin
generalized beta (17.1)
generalized beta-exponential
generalized beta-prime (18.1)
generalized beta type II
generalized Cauchy
generalized error
generalized exponential
generalized extreme value
generalized F
generalized Feller-Pareto
generalized Fisher-Tippett (11.24)
generalized Fréchet (11.28)
generalized gamma
generalized gamma ratio
generalized generalized inverse Gaussian
generalized Gompertz
generalized Gompertz-Verhulst type I
generalized Gompertz-Verhulst type II
generalized Gompertz-Verhulst type III
generalized Gumbel (8.4)
generalized Halphen (20.13)
generalized inverse gamma
generalized inverse Gaussian
generalized K (21.5)
generalized log-logistic
generalized logistic type I
generalized logistic type II
generalized logistic type III
generalized logistic type IV
generalized normal
generalized Pareto (5.2)
generalized Pearson type I
generalized Pearson type II
generalized Pearson type III
generalized Pearson type VII (21.6)
generalized Rayleigh
generalized Sichel (20.14)
generalized semi-normal
generalized-t
generalized Weibull (11.26)
GEV
Gibrat
Gompertz
Gompertz-Verhulst
grand unified distribution
Grassiaunit gamma
greater grand unified distribution (20.1)
GUDgrand unified distribution
Gumbel (8.5)
Gumbel-Fisher-Tippett
Gumbel type N
half-Cauchy (18.9)
half-exponential power (11.4)
half generalized Pearson VII (18.10)
half-LahaSee half generalized Pearson VII (18.10)
half-normal (11.7)
half-Pearson type VII (18.8)
half-Subbotin
half-t
half-uniform
Halphen (20.5)
Halphen A
Halphen B (20.7)
harmonic
Hohlfeld (11.5)
Holtsmark (21.7)
hyperbola (20.6)
hyperbolic secant (15.6)
hyperbolic secant square
hyperbolic sine (14.3)
hydrograph Stacy
hyper gamma Stacy
inverse beta
inverse beta exponential
inverse Burr
inverse chi (11.19)
inverse chi-square (11.17)
inverse cosh
inverse exponential (11.14)
inverse gamma (11.13)
inverse Gaussian (20.3)
inverse half-normal (11.22)
inverse Halphen B (20.8)
inverse hyperbolic cosine
inverse Lomax (13.4)
inverse Nakagami (11.23)
inverse normal
inverse Maxwell (11.21)
inverse Rayleigh (11.20)
inverse paralogistic (18.6)
inverse Pareto
inverse Weibull
Irwin-Hall (21.9)
Johnson
Johnson SB
Johnson SL
Johnson SN
Johnson SU (21.10)
K (21.8)
Kumaraswamy (17.2)
Laha (20.18)
Landau (21.11)
Laplace (3.1)
Laplace’s first law of error
Laplace’s second law of error
Laplace-Gauss
Laplacian
law of error
left triangular
Leonard hydrograph
Lévy (11.15)
Lévy skew alpha-stable
Lévy stable
Lévy symmetric alpha-stable
Libby-Novick (20.10)
log-beta
log-Cauchy (21.12)
log-chi-square
log-F
log-gamma
log-Gaussian
log-Gumbel
log-logistic (18.7)
log-normal (6.1)
log-normal, two parameter
log-Pearson III
log-stable
log-Weibull
logarithmic-normal
logarithmico-normal
logistic (15.5)
logit
Lomax (5.6)
Lorentz
Lorentzian
m
m-Erlang
Majumder-Chakravart
March
max stable
Maxwell (11.11)
Maxwell-Boltzmann
Maxwell speed
Meridian
Mielke
min stable
minimax
modified Lorentzian
modified pert
Moyal (8.8)
Nadarajah-Kotz (14.4)
Nakagami (11.6)
Nakagami-m
negative exponential
noncentral chi (21.14)
noncentral chi-square (21.15)
noncentral F (21.16)
normal(4.1)
normal ratio
Nukiyama-Tanasawa
one-sided normal
parabolic
paralogistic (18.5)
Pareto (5.5)
Pareto type I
Pareto type II
Pareto type III
Pareto type IV
Pearson (19.1)
Pearson type I
Pearson type II
Pearson type III
Pearson type IV (16.1)
Pearson type V
Pearson type VI
Pearson type VII (9.1)
Pearson type VIII
Pearson type IX
Pearson type X
Pearson type XI
Pearson type XII (12.4)
Pearson exponential (20.15)
Perks (20.16)
Pert (12.3)
Poisson’s first law of error
Porter-Thomas (7.5)
positive definite normal
power
power function(5.1)
power prime
Prentice
pseudo-Voigt (21.17)
pseudo-Weibull (11.3)
q-exponential (5.3)
q-Gaussian (19.2)
quartic
Rayleigh (11.10)
Rayleigh-Rice
reciprocal inverse Gaussian (20.4)
rectangular
relativistic Breit-Wigner (9.8)
reversed Burr type II (15.3)
reversed Weibull
Rice (21.18)
Rician
right triangular
Rosin-Rammler
Rosin-Rammler-Weibull
Sato-Tate
scaled chi (11.9)
scaled chi-square (7.4)
scaled inverse chi (11.18)
scaled inverse chi-square (11.16)
sech-square
semicircle (12.8)
semi-normal
Sichel (20.9)
Singh-Maddala
singly non-central F
skew-t
skew logistic
Slash (21.19)
Snedecor’s F
spherical normal
stable (21.20)
stable Paretian
Stacy (11.2)
Stacy-Mihram
standard Amoroso
standard beta (12.2)
standard beta exponential
standard beta logistic
standard beta prime (13.2)
standard Cauchy (9.7)
standard exponential
standard gamma (7.2)
standard Gumbel (8.6)
standard gamma exponential (8.2)
standard Laplace
standard log-normal
standard normal
standard uniform (1.2)
standardized normal
standardized uniform
stretched exponential
Student
Student-Fisher
Student’s t (9.2)
Student’s t2 (9.3)
Student’s t3 (9.4)
Student’s z (9.5)
Subbotin
Suzuki (21.21)
symmetric beta
symmetric beta-logistic
symmetric Pearson
t
t2
t3
tine
transformed beta (18.2)
transformed gamma
triangular (21.22)
triweight (12.11)
truncated normal
two-tailed exponential
uniform (1.1)
uniform difference (21.23)
uniform prime (5.8)
uniform product (10.2)
uniform sum
unbounded uniform
unit gamma (10.1)
unit normal
van der Waals profile
variance ratio
Verhulst
Vienna
Vinci
Voigt (21.24)
Voigtian
Voigt profile
von Mises
von Mises-Jenkinson
waiting time
Wald
wedge (5.4)
Weibull (11.27)
Weibull-exponential
Weibull-gamma
Weibull-Gnedenko
Wien
Wigner semicircle
Wilson-Hilferty (11.12)
Witch of Agnesi
z